Medical Hypotheses 106 (2017) 61–70
The affection of the disturbance of the hydrodynamics of blood in case of
stress on pathological increase of level of low density lipoproteins in
blood. The formation of cylindrical plaques, and their participation in the
development of acute ischemic disorders of heart and brain
S.E. Rusanov
Israel, Haifa
a b s t r a c t
In this article is given the new insight about the affection of stress on the increase of level of low density
lipoproteins (LDL) in the blood, which is connected with the disturbance of hydrodynamics in the bloodstream,
the attention was paid to the cylindrical cholesterol plaque, and it’s classification. The disturbance
of hydrodynamics of blood under the stress leads to the formation of a cylindrical cholesterol
plaque, which repeats the contour of the vessel, and leads to the ischemic disorders of the heart and
brain. The cylindrical cholesterol plaque goes through several stages of development: friable, yielding,
dense, old. In the case of destruction of friable, fresh cholesterol plaque, releases a big quantity of lowdensity
lipoproteins. This leads to the pathological increase of level of LDL in the blood. In the case of long
disturbance of hydrodynamics, occurs the formation of strong links between low-density lipoproteins.
Yielding cholesterol plaque is formed. Further maturation of cylindrical cholesterol plaque, leads to it’s
densifying and damage.
We may emphasize, that short periods of strong contraction and expansion of vessels lead to the
increase of level of LDL in the blood. Self-dependent restoration of normal level of LDL in blood occurs
in the case of restoration of pressure in the limits of numbers, which are specific for particular person,
and which don’t exceed the physiological standard.
Among patients with long duration of stress, the duration of vasospasm increases. LDL, without having
a possibility to crumble, begin to stick together and form the yielding cylindrical plaque. It is characterized
by having of not so strong connection with the vascular wall, and maintains only at the expanse of
iteration of the vascular wall, it has cylindrical shape, is elastic and yellow. The thickness and length of
walls depends on the degree of cross-clamping during the time of formation of yielding cylindrical plaque.
In the case of stopping of spasm, yielding cylindrical plaque can resolve slowly.
Among hypotensive and individuals, which have normal pressure, the increase of level of LDL isn’t
noted. There aren’t such investigations, where such link was noted. The increasing of level of LDL among
these people (especially under the stress) can say about cases of short-term increase of pressure, which
could be unnoticed. These patients require pressure monitoring and, accordingly, the adjustment of the
state of stress and anger.
2017 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Introduction/background
According to the statistics, the frequency of the acute myocardial
infarction over the age of 40 years ranges between 2 and 6
points per 1000 persons in different regions of the world. In the
mature economies of the world the frequency of apoplexy’s contraction
totals, on the average, from 3 to 6 occurrences per 1000
persons [1,2]. Mortality from the apoplexy totals more than 40%
and exceeds the mortality from cardiac infarction.
Most often, the plaque is described, which is covered by fibrin
and which consists of big quantity of lipids, smooth muscle cells
and macrophages with areas of calcification [3]. The increase of
atheromatous plaque begins from proliferation of lipids in the
places of vessel’s ramification, which are exposed to the shear
stress. According to the received opinion, this happens because
macrophages capture lipids and penetrate into the intima of vessels
[4]. Accretions are formed in the form of plaques under intima.
The subsequent sclerosis and calcification of vascular wall leads
to the deformation, luminal occlusion and obturation of vessel
(Fig. 1A(o)). Given plaque has zone of growth in the wall of artery
(Fig. 1A(n)). The vessels germinate through it, which may cause to
bleeding.
Inflammatory change in the vessel wall stipulates ulcers of
atherosclerotic plaques and embolization of arterial trunks by the
products of plaque’s breakdown. At the end of 800s in the XX century
R. Ross proved the signification of inflammation with
atherosclerosis [5]. According to the given hypothesis, the background
of atherosclerosis contraction is infiltration of cholesterol
in the wall of artery, which leads to the peculiar cell-mediated
response of vessel wall and formation of atherosclerosis plaque.
As a rule, atherosclerosis plaque forms from the lipid spot and
begins to increase from the place of origin, and step by step, during
few years, decreases pore. Such plaque, in the given survey, I offer
to call classic atherosclerosis plaque. (CAP) (Fig. 1A).
CAP matures for a long time and subsequently is germinated by
vessels. CAP subsequently increases and overlaps the lumen. Onesided
arrangement of plaque in relation to the vessel is distinctive
(Fig. 1A(n)). The development, appearance and vasodilative mechanism
with the help of such plaques you can see on training video
[6–13].
The solution of problem of the chronic heart disease and the
ischemic stroke, at the moment, is the struggle with risk factors:
hypercholesterolemia, smoking, arterial hypertension, pancreatic
diabetes, obesity [14–17].
Increased content of the cholesterol in the blood was considered
for many years as the primary risk factor of the atherosclerosis,
cardiac infarction, chronic form of chronic heart disease,
cerebral stroke, obliterative atherosclerosis of arteries of lower
limbs. The concentration of total cholesterol in the plasma of blood
and it’s fractions is closely related to the sickness rate and to the
death rate from chronic heart disease. When the concentration of

Fig. 1. 1.A) The vessel with classical atherosclerosis plaque (n). 1.B) Yielding cylindrical plaque during an operation is inside the vessel [49]; 1.C) yielding cylindrical plaque on
the training video follows the contours of the vessel; 1.D) the strong cross-clamping of the vessel creates a strong obstacle to the blood flow and forms the whirling zones (h)
and (i) with sticking of LDL in the front zone (h); 1.E) the sticking of LDL occurs in a view of cylinder with a hole in the middle, and it begins from the place of cross-clamping
of vessel. In the case of imitation of compression of vessel, appears a typical form of closing zone (h); 1.F) the flow with parallel walls; 1.G) the velocity distribution: the
velocity is bigger inside of flow and lower around the vascular wall; 1.H) the weak cross-clamping of the vessel doesn’t create obstacles to the blood flow; 1.I) an obstacle from
one side. Occurs the formation of separation of transit flow and two swirling zones-front (h) and back (i); 1.J) two-component big obstacle creates two pairs of whirling zones
and accumulation of substances in the front (h) and back (i) whirling zones; m – the epithelium of vessel; n – classical atherosclerosis plaque; o – the hole for flow of blood
from one side of the vessel; p – cylindrical plaque; q – cylindrical holes [57].
the total cholesterol is less than 5,2 mmole/l, we can observe the
lowest level of mortality from the chronic heart disease. Increased
mortality among patients with chronic heart disease can be
noticed with the increasing of concentration to 5,3–6,5 mmole/l,
which abruptly increases, when the level of total cholesterol is
7.8 mmole/l. [5]. In different investigations was noted, that the risk
of having of hypercholesterolemia increases with the age and
among people, who used margarine, people, who have obesity,
and among those, who was previously diagnosed on having of
hypertension or diabetes [18]. Lipid-lowering preparations, which
decrease the content of low-density lipoproteins and triglycerides
support stabilization of plaques, and in the process of long-term
application and can support the decrease of their thickness [19].
Close relationship between the increasing of the level of lowdensity
lipoproteins and increasing of the pressure is recognized
worldwide. In the standards of care of such diseases are using
preparations for decreasing of the level of low-density lipoproteins
in the blood [1]; The main reasons of increasing of cholesterol in
the blood aren’t completely investigated. Are known family forms
of hypercholesterolemia, which are inherited. These disorders are
connected with gene-mutation, which encode receptor of lipoproteins
of the low density lipoproteins (LDL).
The plethora of cholesterol in the food, until recently, was considered
as the major factor of development of atherosclerosis,
that’s why was recommended to exclude or to limit products in
the feed, which contain such substance.
Recent investigations refute the given hypothesis. In the 90s has
been described the case with a man, who ate 25 eggs a day and, at
the same time, didn’t have any pathological changes of the level of
cholesterol in the blood. According to the accepted hypothesis, it
couldn’t exist, so he was searched on different mechanisms of
adaptation [20].
The investigations, which has been held in 2015, has shown,
that saturated fats are not connected with the total mortality, vessel’s
diseases, chronic heart disease, ischemic stroke and pancreatic
diabetes of the second type [21]. The chance of fatal case in the
case of the hypercholesterolemia is reasonably high, but is lower,
than for other risk factors, such as arterial hypertension [22]. Other
risk factors can be the reason of great number of cases of cerebral
circulation disturbance [23].
There are cases of cardiac infarction without determining of the
arterial sclerotic disease of the coronary arteries [24]. You can
observe a cardiac infarction with normal coronary vessels, it totals
5–25% of all cases of acute myocardial infarction [25,26]. The consumption
of alcohol can influence on the level of cholesterol in the
blood and on the development of hypertension [27]. Exists the connection
between the hyperlipidemia and the ‘‘cardi
ophyshoneurosis” [28,29] studies. Modern investigations change
the opinion about the reasons of the appearance of atherosclerotic
plaques.
The investigations, which have been done in 2014, have shown
that there is no connection between the pancreatic diabetes and
changes in the histology of plaque and wasn’t detected any differences
in the expressiveness of the inflammatory components in the
plaques of patients with pancreatic diabetes and without diabetes
[30]. There weren’t found the investigations, where we could
observe the connection of hyperlipidemia among people with the
hypotension and among people with normal numbers of arterial
pressure.
So, real causes of pathological increase of the level of lowdensity
lipoproteins in the blood, among people without problems
with genes, still aren’t determined. At the same time, all the previous
and recent investigations find the close relationship between
the hyperlipidemia and increase of pressure.
The hypothesis about primary inflammation of the vessel wall is
one of the most common hypothesis about the trigger of
atherosclerosis. There are a number of consecutive stages of forming
of atherosclerosis plaque: dysfunction of endothelium, adhesion
and diapedesis of monocytes, formation of foam cells,
migration and proliferation of smooth muscle cells. According to
the author’s opinion, atherosclerosis represents the range of
highly-specific cellular and molecular changes, which are better
to be considered as an inflammatory disease [31–33].
In 1965, Miasnikov proposed the hypothesis that takes into consideration
not only the lipid metabolism, but also the state of the
vessel’s wall by combining both of these factors [34].
Also, one of the reasons of cardiac infarction is considered to be
stress. Predisposition for felling the anger on minimal provocations
(Angry Temperament) and predisposition for expressing the anger
outside (Anger-Out) influences on the atherosclerosis of the carotid
arteries [35]. The presence of atherosclerotic plaques depends from
the stress, depression, qualm [36]. Acute coronary syndromes
depend from emotional triggers, which represent the events of
national importance, such as earthquakes, terroristic attacks,
financial crisis, and also individual experience of acute anger, stress
and depression [37,38].
During the 60-day period after 11 September 2001, was
detected statistically significant increase in the number of patients
with acute cardiac infarction [39,40]. In the process of long-term
rehabilitation, the symptomatology of myocardial ischemia disappears
[41]. Many patients in my practice have noted, that clinical
implications have appeared in the coming days after beginning of
stress.
If the stress continues for a long time, the clinical implications,
not only don’t decrease, but also strengthen. Dr. Jiang Wei (Wei
Jiang) and colleagues in 2013 have studied the effect of escitalopram
on the myocardial ischemia. In the given analysis, attention
was paid to the ischemia, which is caused by the physical exertion
and stress. In the conclusion scientists note that ischemia in the
consequence of the mental stress is more common phenomenon,
than it was previously presumed.
It is important, that the signs of ischemia occurred in very short
period of time after the stressor [42]. Was demonstrated, that
among patients with coronary artery disease, psycho-emotional
excitation and emotional stress factors can be reliably releaser of
contraction of myocardial ischemia [43].
In the given article I offer to consider the special type of plaque
more attentively, which is considered as rarer variety – «soft» plaques.
According to my opinion, this type of plaque helps to understand
the mechanism of rising of cholesterol level in blood among
patients without abnormality in genes and development of acute
ischemic manifestations under the stress.
Exactly the presence of yellow plaques some authors connect
with emergence of acute coronary syndrome [44]. L. O’Holleran
and others suppose, that «soft» or heterogeneous plaques to the
fullest extent support the development of ischemic stroke [45].
The hypothesis/theory
One of the main reasons of apoplexy’s development is the
stenosis of the carotid artery [1,14,46]. The main reasons for the
cardiac infarction are atherosclerosis and atherothrombosis. The
patient, which had an atherothrombotic stroke, has increased the
risk of repeated action in the same or other vascular pool [4].
During the period of my studying at the institute (1988–
1994 year), and later in my practice, I have seen that the generally
accepted norms, which recognize food cholesterol as the releaser of
vascular heart disease, don’t work in practice.
Healthy people ate lot of eggs per day, consumed large amount
of tallow oil and fatty meat, and thus, had no problems with blood
vessels, heart and brain.
In contrast, in the case of occurrence of problems in the family,
at work, etc., as a patient in the coming days and weeks turned out
to be in the hospital with problems of heart and brain.
Many patients, which are under the treatment, and which are
on a strict diet, which doesn’t include cholesterol, had elevated
levels of cholesterol in the blood. Among hypotensive patients,
and among individuals with the normal blood pressure, in which
the pressure didn’t rose above the physiological standard (PS),
the level of cholesterol in blood was always within the PS, not
dependently of cholesterol of food. The increasing of blood level
of LDL among hypotensive patients, and among patients with normal
blood pressure, was accompanied by a short-term increase in
pressure above the PS.
This information gave me the opportunity 20 years ago to put
forward a hypothesis that stress leads to an increase in blood pressure,
and that the increase of pressure leads to the increase of LDL
in the blood. Recent investigations have confirmed the absence of
close relationship between food intake, which contains cholesterol,
and diseases of cardiovascular system. The diet only in conjunction
with statins, decreases the level of LDL in the blood [47]. Modificated
diet (with decrease of quantity of fat) may have a hypotensive
effect among patients with diabetes and with moderate
arterial hypertension. However, the degree of reduction of blood
pressure allows to presume, that given diet may be considered,
at the best, only as addition to the traditional antihypertensive
medical therapy [48].
All the afore-mentioned factors indicate, that the accepted theories
of increasing of level of low-density lipoproteins are contradictory
and don’t reveal the precise mechanism, which leads to
the increase of level of LDL in the blood.
In the given article, I propose a hypothesis, which was elaborated
by me, that can answer the questions, why the level of LDL
increases in the blood, and why the stress leads to the formation
of plaques, which are different from the classical atherosclerotic
plaque (CAP).
In the process of attentive video’s review, which was filmed
during the performance of carotid endarterectomy [49], we can
see the plaque, which is not similar to CAP. The location of given
plaques is the same among all people [49–57]. On the giving
video we can see cholesteric plaque of yellow color, which is
elastic, has cylindrical form, which follows the contour of vessel,
has approximately the same thickness all around and has the
hole in the middle and blood passes through it (Fig. 1-B(p)). In
the process of few operations, the plaque easily can be separated
from the wall and easily can be removed in the form of cylinder
from the vessel [49]. On the teaching video, which is dedicated to
the operation on femoral artery the plaque appears in the form of
cylinder and specially elaborated cylindrical instruments for making
of exfoliation of such plaque from the vascular wall [50]. On
the teaching video, concerning the stenting of vessels, on the section,
you can see walls of plaque, which have cylindrical form
[51]. I offer to call them cylindrical plaques (CP). Easy exfoliation
from the wall emphasizes, that given cylindrical plaque is located
not under vessel’s intima, but from above it. «Older» cylindrical
plaques firmly secure with the intima, the thickness becomes
irregular, vascular invasion is visible, occurs necrotizing, and it
requires bigger efforts in order to separate the cylindrical plaque
from the vessel [52]. Sometimes splitting of the vessel wall is
required in the process of eradication of cylindrical plaque
[53–55]. Also are visible old ulcerated cylindrical plaques [56].
During the classes on pathological anatomy, in the process of
human’s autopsy, who had died from acute infarction, we
observed great number of such cylindrical yellow plaques, which
easily could be separated from the vessel’s wall and were
situated in the different places of large arteries [57]. In the process
of autopsy of bodies of heavy drinkers, the plaques weren’t
found. With words of teachers, such situation occurred in their
practice in the majority of cases.
I propose the classification of given plaques, and the way of
recovery of normal level of LDL in the blood.
For this purpose, some important features should be
distinguished:
- The increase of pressure and increase of the level of LDL in the
blood are closely connected: the LDL level is always elevated
among individuals with high blood pressure, and is absent
among people with hypotonia and with normal level of
pressure.
- The stress and diseases of cardiovascular system are closely
connected: stress, qualms, anger, etc., cause the increase of
pressure, ischemic disorders.
- The short time interval between the beginning of stress and the
appearance of clinical symptoms: it takes few days or weeks
from the beginning of the stress to the appearance of clinical
symptoms in a patient, at the same time is proved, that classical
atherosclerotic plaque gathers for years and decades, and cannot
«gather» for few days.
- The formation of cylindrical plaque in one and the same places
among different patients: the presence of involvement of extra
cranial arteries, in certain places, disproves the opinion about
inflammatory process, which has occurred accidentally, as triggering
factor of affection of vessel wall.
- The cylindrical shape of plaques in the case of acute processes
in the myocardium and brain: a prominent feature of atheromatous
plaque is a cylindrical shape with a hole in the middle,
with a uniform wall thickness, which follows the contour of
the vessel. This plaque is not similar with CAP.
- Different degree of addition, invasion and damage of the plaque:
during the operation is possible to see plaques, being on
the different stages of attachment to the artery.
- Different length of cylindrical plaque: cylindrical plaque can
have different length, but the cylindrical shape is maintained.
The plaque in the femoral artery also has a cylindrical shape,
and is elongated along the vessel.
- The blood flows within the cylindrical plaque along its entire
length: classical atherosclerotic plaque increases from one side
of the vessel, and the blood rounds her, and presses to the opposite
vascular wall (Fig. 1-A(o)).
- The involvement of heart and brain occurs in one and the same
time: the coincidence of time of pathology of heart’s vessels and
brain’s vessels is difficult to be explained by maturation and
destruction of few classical atherosclerotic plaque.
- The damage of the heart and brain without finding the plaques:
this can be, if there is a plaque, which has enough time to dissolve
before the examination or autopsy.
- The cylindrical plaques can be found in the certain vessels:
Cylindrical plaques can be found, mainly, in the arteries, which
have average and large diameter, and which have muscular
fibers. There is no information about the formation of atheromatous
plaques in veins.
- The nerves, which innervate the vessels, have the certain entry
points into the vessel wall: entry points are located sectionally.
Then occurs the formation of perivascular plexuses, from which
the fibers spring and penetrate into the vascular wall [58]. The
compression of vessels in such situation can occur sectionally,
in the points of nerve’s entry inside the vascular wall. We can
presume, that there are places with the greatest degree of
cross-clamping.
- The change of clinical implications, depending on the duration
and the intensity of the stress factor: in the case of continuation
of stress determines recrudescence, the overlay of disturbances
in other organs. In the case of decrease of stress, the decrease of
clinical picture of ischemia can be observed.
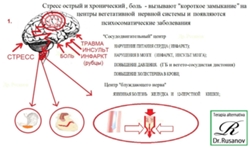
From all has been said we can make the assumption that stress
causes the overexcitation of cells of central nervous system. In the
process of reaching of the certain level of excitation in the central
nervous system occurs the formation of new pathological ways of
propagation of electrical pulses. Such pulses can pass from the central
nervous system to the autonomic nervous system, and can
affect on the vasomotor center, center of the vagus nerve and other
centers, causing disturbances in work of the somatic organs. Therefore,
such diseases are called ‘‘psychosomatic.”
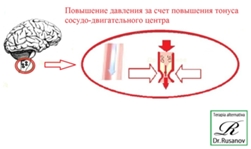
The arrival of pathological electrical pulse (PEP) on the vasomotor
center leads to the vasospasm in the areas of perivascular
plexuses and to the increase of pressure. If the PEP takes a lot of
time – the spasm occurs in the long-term, if the PEP has bigger
force – the vessel constriction and the increase of pressure is
bigger.
In the case of decrease of the stress factor, cell firing of Central
Nervous System decreases, the quantity and the force of PEP
decreases. The vasomotor center decreases impact on the vessels,
and the pressure decreases.
In the case of frequent and strong compression of vessel may
appear damaged areas of muculent vascular wall with appearance
of areas of inflammation. In these places, in the future, the classical
atherosclerotic plaques can be formed. Also, in this place, begins
the growth of other plaque, which, according to it’s all characteristics,
is different from the classical atherosclerotic plaque.
Here takes the beginning the cylindrical plaque (CP) (Fig. 1-B,
-C). The CP goes through several stages in it’s development.
I offer to fix such stages of development of cylindrical plaque:
– friable cylindrical plaque (FCP);
– yielding cylindrical plaque (YCP);
– dense cylindrical plaque (DCP);
– old cylindrical plaque (OCP);
Let’s consider in more detail the yielding cylindrical plaque. The
given plaque contains a big amount of lipids, and has thin
connective-woven capsule, which is not yet fused with the wall,
and can be separated completely from the epithelium, without
damage of the vessels wall (Fig. 1-B). Around yellow plaques are
located T-lymphocytes, which secrete gamma interferon, which
prevents the strengthening of the fibrous capsule of plaque.
The thin shell of the YCP can be damaged in the connection with
affection of hemodynamic factors, and other impacts [59]. This
suggests, that YCP can be easily formed (shaped), as well as, under
certain conditions, can be easily dispersed. The presence of hole in
the middle of the cylindrical plaque (Fig. 1-B(q), -C(q)) indicates
that the increase of cholesterol yellow plaque follows the periphery,
close to the vascular wall and forms the ring.
We can assume that the YCP consists of a large number of annular
plaques, which are fastened between themselves. Every subsequent
layer extends YCP, gives the appearance of cylinder to it,
with the preservation of the vessels configuration. Such plaques
are painted on a training video on stenting, and can be seen during
the operation of removal of atheromatous plaque [49–56].
In the case of amplification of stress, the clinical implications
among patients are increasing, and it says about the increasing of
size of cylindrical plaque. In the case of reducing of stress, and after
the recovery period, the clinical implications, as the rule, are reducing.
Thus, it can be assumed, that patients, which are undergone to
the stress, after increase of pressure, may have YCP, which may
have, in the future, two principal ways: or to continue their own
development, or gradually dissolve.
The ability of plaque to dissolution may help to understand
why increases the level of LDL. In order to understand this mechanism,
should be considered the earliest form of the cylindrical
plaque, friable cylindrical plaque (FCP). In the case of sharp and
strong compression of the vessel forms the sharp obstruction to
the blood flow. Before the obstruction the LDL begin to accumulate
(Fig. 1-D). Hemodynamic causes of this phenomenon will be
described later. Above the place of cross-clamping are forming
swirl zones. During the formation of the CP exists a certain, very
short period of time, when the LDL are accumulating in the front
of obstacle, are holding on each other at the expense of their
structure.
At the present time, the strong links between the LDL don’t
exist. LDL in the given plaque are in the state of weak stable balance.
They can’t move to the bloodstream because of obstacle
and they haven’t agglutinated between themselves. So, there are
a lot of places, where vessels clamp abruptly, at the same time a
big quantity of friable cylindrical plaques.
At this stage, the friable cylindrical plaque is difficult to be
detected because of the short cycle of existence. Clinically, they
also don’t implicate, because the accumulation of LDL can’t block
the lumen more than blocks the lumen of the stenosed vessel. During
the initial period of stress and effort syndrome, increased pressure
has the short-term nature. After the vasospasm occurs the
vasorelaxation. The vascular geometry restores. After the aneurysm
the border of plaque moves to the whirl zone and friable cylindrical
plaque crumbles.
Now it is necessary to consider the mechanism of changing of
the level of LDL in the blood. After the forming of few friable cylindrical
plaques the quantity of LDL in blood decreases abruptly. In
response, the hepatic cells synthesize LDL with the purpose of
increase of level of LDL in blood to the PS. In the case of abrupt
vasodilation LDL begin separating from FCP and they return into
the bloodstream.
After the breakdown of all friable cylindrical plaque, the LDL are
circulating in blood, which were synthesized by the hepatic cells
and cells of LDL, which were deponed into the friable cylindrical
plaque. The level of LDL in blood becomes above the physiological
standard.
In order to increase the level of LDL in the blood, must be one
very important condition. The vasospasm must stop until, when
the connection between LDL forms, and which is able to keep
LDL together. Several factors affect on the degree of increasing of
level of LDL: the quantity of FCP, the duration of compression of
vessel, the force of compression of vessel, quantity of LDL in FCP,
the quantity of LDL, which was synthesized by the liver before
the decay of FCP.
The utilization of LDL occurs much slower in contrast with the
synthesis, so reducing of level of LDL to the normal numbers
requires a long time. If, during this time, will happen again the
cycle of compression-engorgement of vessels, the level of LDL will
increase again. If the person at this time will eat the product, which
contains cholesterol, the level of LDL in blood will also increase. It
will take more time for it’s utilization, and reduction of the normal
level of LDL. The limitation of cholesterol, which is coming from
the food, is justified during this period. 1 g. of cholesterol is synthesized
and about 0.5 g of it comes with food. All quantity of cholesterol
is used during the day [60].
The reception of statins is also partly justified, but requires high
pinpoint accuracy, so very strong limitation of synthesis of LDL can
lead to the shortage of LDL and to the further malfunction in work
of organs and systems.
In the case of stable pressure over a long period of time, the
level of LDL in the blood is stabilized independently.
Among hypotensive and individuals, which have normal pressure,
the increase of level of LDL isn’t noted. There aren’t such
investigations, where such link was noted. The increasing of level
of LDL among these people (especially under the stress) can say
about cases of short-term increase of pressure, which could be
unnoticed. These patients require pressure monitoring and,
accordingly, the adjustment of the state of stress and anger.
The increasing of level of LDL in the blood among hypotensives
can be expected only when the stress will lead to the increase in
pressure above the physiological standard. The adjustment of
stress among hypotensives must be started immediately, in case
of increasing of level of pressure above their normal rates, and in
case of normal level of LDL in the blood.
The change of pressure indicates that the problem in the central
nervous system and autonomic nervous system already exists. In
the case of absence of adjustment of stress, we can expect farther
increasing of pressure. When the pressure increases above the
level of physiological standard, the level of LDL in blood will
increase.
Among hypertensive, which take medicines on a regular basis,
there may be periods of lack of medicines for various reasons: skipping
of the next dose, early termination of medicine’s action, which
is connected with incorrectly selected dose, with addiction to the
drug or it’s more rapid destruction, etc. At this time, among such
patients, the pressure may increase. Patients, which are on the
strict diet without cholesterol, in such circumstances, may have
elevated numbers of level of LDL. The increasing of level of LDL
in the blood, among such patients, can be considered as an occasion
for reviewing and changing of the regime of treatment of
hypertension.
Among patients with long duration of stress, the duration of
vasospasm increases. LDL, without having a possibility to crumble,
begin to stick together and form a yielding cylindrical plaque
(YCP). It is characterized by having of not so strong connection
with the vascular wall, and maintains only at the expanse of iteration
of the vascular wall, it has cylindrical shape, is elastic and yellow.
The thickness and length of walls depends on the degree of
cross-clamping during the time of formation of YCP. In the case
of stopping of spasm YCP can resolve slowly.
During the fastening with intima of vessel and in the process of
crystallization, the plaque becomes denser. The formation of dense
cylindrical plaque (DCP) takes place. It is characterized by the fact,
that the removal requires a strong mechanical impact, and splitting
of the vessel wall.
During the invasion of such plaque with help of vessels, and in
the process of further crystallization, – old cylindrical plaque (OCP)
forms. It is characterized by the fact, that in it’s wall occur nonreversible
changes: the thickness of plaque changes, burstings
appear, and places of necrosis and ulceration [56]. All the processes
occur in the same way, like in the classical atherosclerotic plaque,
with one very important difference. The damage of cylindrical plaque
can occur in it’s different places.
One of the places, where the cylindrical plaque can be damaged
most often, is the place of cross-clamping. At this place, the CP may
have a sharp edge, which can be explained by difference in the
geometry of the ‘‘quiet” and ‘‘compressed” vessel. If in the given
place we change the geometry of vessel (the decrease of diameter),
we can see, that the form of plaque coincides with the deflection of
the vessel (Fig. 1-D), and an inner diameter corresponds to the
diameter of lumen of plaque.
After the crystallization of wall of plaque, the change of geometry
of vessel leads to the deformation of edge of plaque, and it’s
separation from the vascular wall. In the future, in this place develops
inflammation, bleeding, necrosis.
The detailed hemodynamic changes that lead to the formation
of a cholesterol plaque in the form of a cylinder will be described
below. In the case of sharp cross-clamping of the vessel, conditions
for the formation of zones with fluid whirls are creating. The speed
of moving of formed elements of blood in the given zone slows,
down to the full stoppage. For the reason that compression of vessel
occurs in the form of ring, LDL stay in zones on the perimeter of
vessel. The obtained ring from LDL, in turn, creates new whirl
zones. The length of plaque gradually increases. Blood flows inside
of formed aggregation of LDL. Whirl zones form near the walls of
vessel and repeat it’s contours. If the compression of vessel takes
more time, the process of formation of cylindrical plaque lasts
longer. If the compression of vessel is stronger, the thickness of
walls of cylindrical plaque is bigger. Initially, occurs the formation
of friable cylindrical plaque, in the future occurs the formation of
yielding cylindrical plaque.
Let’s consider the hydrodynamic principles, which lead to the
formation of CP.
Blood is a viscous fluid. According to the hydrodynamics, fluid
has two basic properties. It changes it’s volume seldom in the case
of changing of pressure, and has fluidity, and takes the form of a
vessel, in which it locates.
Under the normal conditions, fluids in cylindrical vessels have
two types of flow: laminar and turbulent. Water, in contrast with
the blood, often flows turbulently. Blood relates to a viscous fluid.
On average, the relative blood viscosity is almost 4,5 (3,5–5,4).
The flow of blood in vessels, most of all, has the laminar type.
According to some authors, under the physiological conditions,
turbulent flow of blood may be in the places of natural division
of the arteries. In the pathological conditions the turbulent flow
can be detected in the places of stenosis, blocking, in the case of
passing through defects, and also in the case of reduction of the
blood viscosity (anaemia, fever) and during the physical load [61].
In the laminar and turbulent flows, the velocity of distribution
of fluid in the vessel with parallel walls is irregular. It is described
by para-curve, which is more elongated in a laminar flow (Fig. 1-G).
The peripheral area of the blood, which adjoins to the walls, has the
lowest speed of motion. In the blood, occurs a constant mixing of
layers with the help of red cells. Most of the red cells float in the
central stream, where the speed is maximal. Different hydrodynamic
forces affect red cells and make them to revolve and move
in different layers of blood. It supports the movement of substances
into different layers of blood, which are dissolved in the
plasma [62].
In the case of hypotension diameter of vessel is not changed
(Fig. 1-G). The flow of blood in case of hypotension is the same
as in the pipe with parallel walls.
For the regulation of pressure in blood-vascular system there
are arteries of muscular type, which can, at the expanse of changing
of tonus of unstriated muscles, change the diameter of vessel
and increase the hydrodynamic resistance of blood. The vessel
compresses the most strongly in certain places. In the case of pressure
within the limits of physiological standard, the diameter of
the vessel is slightly reduced (Fig. 1-H).
If the pressure increases above the physiological standard,
appears an obstacle to the blood flow, which is described in
hydraulics as ‘‘sudden contraction”, which is approximately the
same, if you put a ring with small hole in the middle of pipe.
(Fig. 1-D).
The hydrodynamics considers different types of barriers, and
different models of behavior of fluid, depending on the ratio of
the diameter of vessel and obstacles. In the case of slight change
of the diameter, blood flow doesn’t change. The slight curvature
of flows near the wall occurs, with a slight acceleration of the
speed in the middle of the vessel (Fig. 1-H). In the case of decrease
of diameter to the smaller extent, the movement changes abruptly
(Fig. 1-D). This is because that the fluid must pass through the hole
much less than the diameter of the vessel before the obstacle. The
entire mass of the liquid must squeeze through the narrow hole. A
big quantity of uniformly moving blood supports behind. The liquid
from the wall layers tends to penetrate into a narrow hole,
and occurs so-called « separation of transit flow » from the vascular
wall, with formation of zones with fluid whirls.
The front area appears in the parietal space in front of an obstacle
(Fig. 1-J(h), -D(h)).
The rear zone is formed behind the obstacle (Fig. 1-J(i), -D(i)).
After passing of certain distance, the flow expands gradually, and
layers of blood return to the vascular wall. The formation of
whirling spaces occurs in the case of laminar and turbulent flow
[62–64].
In the places of whirl longitudinal velocity of flow slows down
abruptly, and sometimes has the opposite direction. For the reason
that the velocity of flow is slow, in these areas, exists the possibility
for the accumulation of substances with certain chemical and
physical properties (Fig. 1-J(h), -D(h)). LDL, apparently, have such
properties.
Such phenomenons occur in the environment. So on the rivers,
in front of big obstacle, the rubbish of all kinds accumulates, and
during a snowstorm the snowdrifts are forming until and after
obstacle [65].
Prolonged compression of vessels leads to the pasting together
of LDL, and to the formation of the yielding cylindrical plaque
(YCP), which repeats the contours of vessel.
The stages of change of pressure, and connected to it the subsequent
change of level of LDL in the blood.
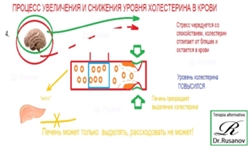
In the case of constant low pressure, there aren’t damages of
hemodynamics, the level of LDL in blood is regulated by hepatic
cells in the limits of physiological standard (Fig. 2-2.1).
In the case of pressure in the limits of physiological standard,
occurs easy deformation of flow layers with small velocity increase
in the middle of flow. The level of LDL in blood is regulated by hepatic
cells in the limits of physiological standard (Fig. 2-2.2).
If the pressure exceeds the physiological standard, the contraction
of muscular ring leads to the formation of a strong obstacle,
which is described in hydraulics as ‘‘sudden contraction.” In the
short period of time, before the deposition of LDL, their level in
blood is normal (Fig. 2-3.1). LDL are accumulating in front of obstacle,
the friable cylindrical plaque is forming, the level of free LDL
begins to decrease in the blood (Fig. 2-3.2). The number of LDL
increases in the friable cylindrical plaque, and the level of free
LDL in the blood decreases (Fig. 2-3.3). In the case of decrease of
level of LDL in the blood below the physiological standard, the liver
cells begin to synthesize LDL and restore the level to the level of
physiological standard (Fig. 2-3.4). The level of LDL in blood is regulated
by hepatic cells in the limits of physiological standard
(Fig. 2-3.5).
In the case of decrease of pressure (the expansion of vascular
wall) (Fig. 2-4.1) occurs a rapid destruction of friable cylindrical
plaque. The level of LDL in the blood begins to increase (Fig. 2-
4.2). In the case of destruction of all FCP, the level of LDL in the
blood reaches a maximum. This level is higher in contrast with
physiological standard, and may have different indicators, even
in the same person at different time (Fig. 2-4.3). Synthesis of LDL
with the help of liver cells is absent before the reduction of level
of LDL in the blood within the physiological standard. The level
of LDL in the blood is gradually decreased (Fig. 2-4.4). In the case
of reaching of level of LDL in the blood to the level of physiological
standard, the liver cells begin to regulate the level of LDL again
(Fig. 2-4.5). In the case of reduction of pressure, for a long time,
the level of LDL in blood is regulated by hepatic cells in the limits
of physiological standard (Fig. 2-4.6).
In the case of full restoration of the normal level of pressure,
without cycles of compression – expansion of vessels, the level of
LDL is regulated by liver cells within the physiological standard
(Fig. 2-5.0).
We may emphasize, that short periods of strong contraction and
expansion of vessels lead to the increase of level of LDL in the
blood. Self-dependent restoration of normal level of LDL in blood
occurs in the case of restoration of pressure in the limits of numbers,
which are specific for particular person, and which don’t
exceed the physiological standard.
Evaluation of the hypothesis/idea
The hypothesis allows to understand the mechanism of formation
of cylindrical plaques, which hadn’t been previously described
and which are different from the classical atherosclerotic plaque.
The formation of the cylindrical plaque occurs according to another
scheme. These plaques are the reason of the acute ischemic attacks
of heart, brain, vessels in terms of the acute, severe stress and can
disturb the essential regulation of the LDL in blood, which leads to
the pathological increase of low-density lipoproteins in blood. Such
plaques appear during the short period of time, in the contrast with
the classical plaques, which were developing for many years. Few
days of severe stress is enough for forming of cylindrical plaque.
The hypothesis explains, why the level of LDL increases in blood
under the short-term increase of pressure and under the hypertension.
The hypothesis completely explains the mechanisms of
increasing and decreasing of symptoms of the ischemic attacks of
heart and brain in terms of increasing and decreasing of stress.
The hypothesis explains, why the increasing of LDL can’t be
observed among « the clear » hypotensives. The hypothesis
explains, why even under the strict diet without cholesterol the
level of LDL may increase among patients.
Because of the monitoring of the level of cholesterol in blood is
possible to change the ways of treatment of the hypercholesterolemia,
to reconsider the duration of administration of drugs,
which decrease the level of pressure and the level of LDL in blood.
According to this hypothesis the doctor, in the process of
observing of the cholesterol’s level in blood, can control the correctness
of the prescription of drugs from pressure and monitor
the correctness of drug’s taking by the patient, can diagnose the
diseases in a timely manner, which are connected with the
short-term increase and decrease of pressure, even in the case of
absence of another symptoms, can predict the appearance of plaques
in the places of the cross-clamping and appearance of the
acute ischemic disturbances of heart and brain, which the patient
has, being under acute, strong stress, the hypothesis allows to take
into consideration the short time from the beginning of stress to
the emergence of symptomatology and permits to render the aid
for patients, who undergo the acute stress. The hypothesis allows
to submit the complete information for patients about the risk
for feeding of heart and brain, which is connected with the acute
stress with the purpose of the application of measures in order
to reduce the stress.
Consequences of the hypothesis and discussion
The proposed hypothesis more fully reflects the mechanism of
abnormal increase of level of LDL in the blood. Were disclosed
cause-effect relations between stress, short-term increase of pressure
and an increase of level of LDL in the blood; between stress
and ischemic disorders in heart and brain. Was described the
mechanism of formation and stages of development of cylindrical
plaque (CP). Was given an explanation for the reasons of increasing
of the level of LDL among hypertensives, who are on the strict diet
without cholesterol. Was explained the absence of increasing of